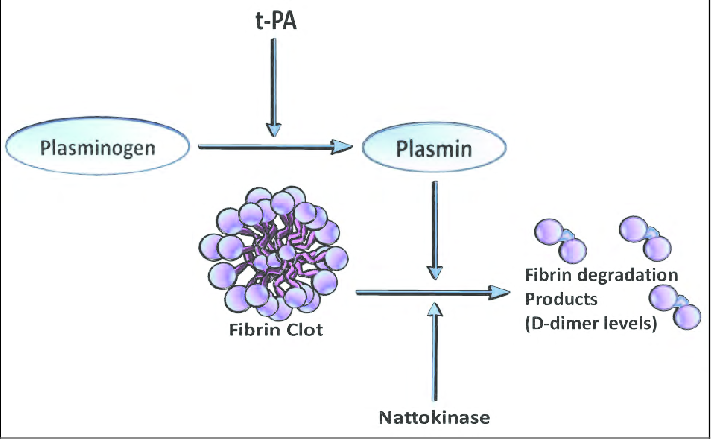
Are Fibrinolytics Key to Preventing Clogged Arteries?
The anti-cancer supplement berberine may be another treatment candidate. Research has shown that spike protein levels decrease in COVID-19 patients treated with the therapeutic.
This promising research suggests that recombinant spike and envelope SARS-CoV-2 proteins were disrupted by BromAc. Spike and envelope protein disulfide bonds were reduced by Acetylcysteine.
None of the substances mentioned can be expected to accomplish a full reversal of vulnerability, risks and in some cases outright injury inflicted by the COVID vaccines, but one or more may possibly be effective enough for some people. As always, consult your local healthcare provider for your optimal individualized plan.
Dr. Paul Marik and Dr. Pierre Kory are pleased to introduce the I-RECOVER: Post-Vaccine Treatment protocol, designed to help people who have experienced adverse symptoms after a COVID vaccine.
Specific treatments:
In summary, the combination of curcumin and bromelain are well positioned as supplements in people who are getting repetitive COVID-19/Spike protein exposure. Future randomized trials will elucidate the clinical benefits in specific applications.