Is Polio Eradication by Vaccine a Myth?
Polio and smallpox: vaccines saved us!!
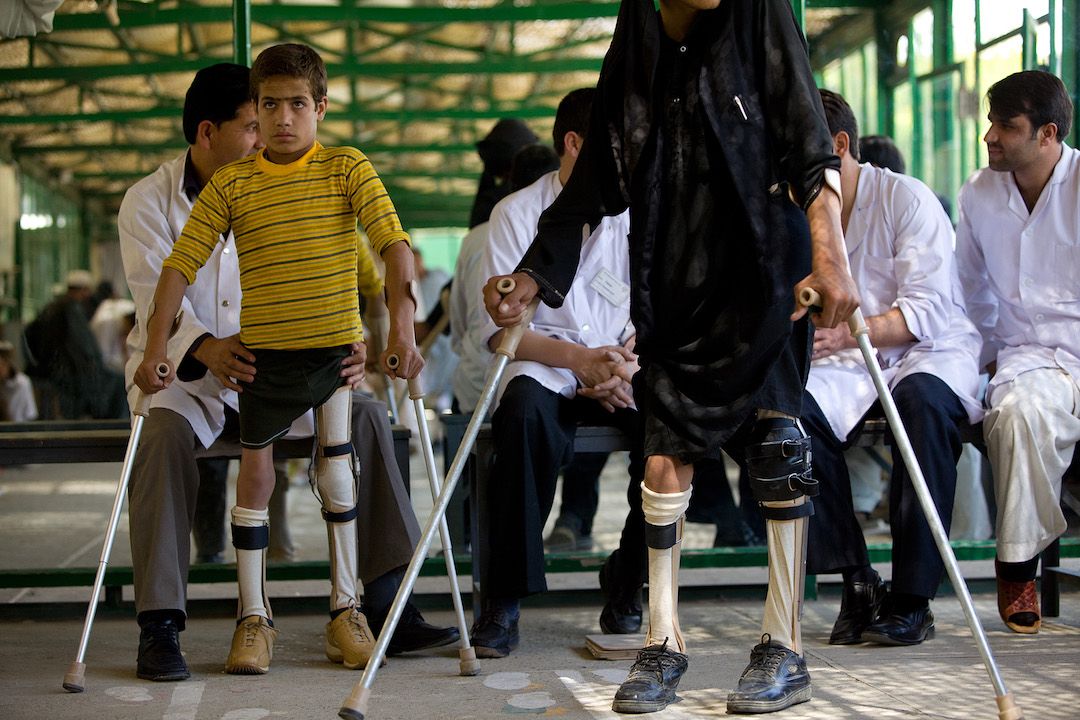
Inevitably, this is the first reason brought up in conversation to explain why vaccines are essential. The image immediately conjured up is of iron lungs and calipers on poor defenseless children in a hideous epidemic. The vaccines of Sabin and Salk supposedly led us to freedom from this dreaded illness.
Points of discussion:
-
Polio is generally just a mild respiratory illness.
-
Intramuscular injections of antibiotics to counter pneumonia appeared to cause paralysis.
-
Inoculations of live polio caused paralysis, which is why they changed to an oral polio vaccine (OPV) by a spoon or sugar cube.
-
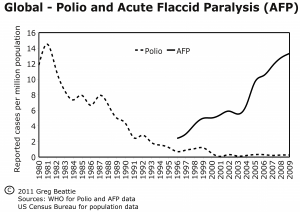
Polio never went away. It was redefined as ‘acute flaccid paralysis‘ , Guillian Barre Syndrome etc.
-
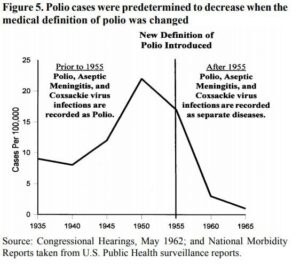
After mass vaccination, diagnosis of polio was changed from an upper respiratory illness to a paralysis greater than 60 days, making many polio diagnoses disappear.
-
Before this reclassification, polio was just a flu-like illness and paralysis was quite rare.
-
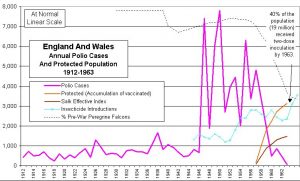
Polio has not been eradicated, particularly from poorer countries, and is now predominantly ‘vaccine-derived polio’.
-
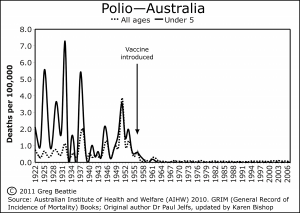
The vaccine was introduced after the incidence of polio deaths had dramatically declined.
Acute flaccid paralysis surveillance indicators in the Democratic Republic of Congo during 2008-2014
Vaccination Dilemma – Understanding the Vaccination Debate
Research/Articles:
2 October, 2025 – Eight Suppressed Truths About The Decline Of Polio
Global vaccination campaigns are credited with reducing polio cases by 99 percent since 1988, and the world stands on the brink of eradication thanks to this “miracle” intervention.
But is this rosy story the full truth? A growing body of evidence—historical data, medical literature, and testimony from experts—suggests the conventional polio narrative is incomplete, if not flat-out wrong, on multiple counts.
This report takes a hard look at polio’s history and the vaccine campaign, uncovering eight key underreported facts that challenge the dominant narrative.
1. Changing the Diagnosis: How Polio “Disappeared” on Paper
2. Poisoned Paradigm: The Toxic Link to Polio-Like Paralysis
3. Dissolving Illusions: Dr. Suzanne Humphries and the Forgotten History
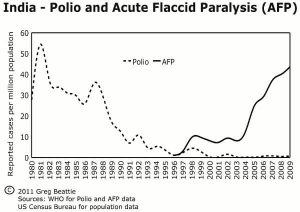
4. The Indian Enigma: Polio’s Decline, Paralysis’s Rise
5. When the “Cure” Causes the Disease: Vaccine-Derived Polio Outbreaks
6. A Harmless Passenger? Polio Virus as a Commensal Microbe
7. Ethical and Legal Concerns: Eradication at All Costs?
8. The Untold Story: Sanitation, Nutrition and Polio’s Decline
Eight Suppressed Truths About The Decline Of Polio _ Principia Scientific, Intl_.pdf
4 April, 2025 – How Polio Fails Koch’s Postulates
In the late 1800s, German bacteriologist Robert Koch developed four postulates, which outline a set of logical criteria necessary to establish that a microbe causes a specific disease.
They emphasize association, isolation, causation, and re-isolation. While phrased slightly differently in various sources, the postulates are most commonly stated as follows:
-
The microorganism must be found in abundance in all cases of those suffering from the disease, but should not be found in healthy subjects.
-
The microorganism must be isolated from a diseased subject and grown in pure culture.
-
The cultured microorganism should cause the same disease when introduced into a healthy subject.
-
The microorganism must be reisolated from the inoculated, diseased experimental host and identified as being identical to the original specific causative agent.
Postulate 1: The microorganism must be found in abundance in all cases of those suffering from the disease, but should not be found in healthy subjects. – “During an epidemic of poliomyelitis in Michigan in 1958, virological and serologic studies were carried out with specimens from 1,060 patients. – Fecal specimens from 869 patients yielded no virus in 401 cases, poliovirus in 292, ECHO (enteric cytopathogenic human orphan) virus in 100, Coxsackie virus in 73, and unidentified virus in 3 cases. – Serums from 191 patients from whom no fecal specimens were obtainable showed no antibody changes
Postulate 2: The microorganism must be isolated from a diseased subject and grown in pure culture.
In 1949, a man named John Enders developed a technique for allegedly cultivating the polio “virus” in vitro. He observed some chemical reactions in a cell culture, and proclaimed that a virus was present.
However, such a procedure does not represent the isolation of a pathogen in a pure culture, as acknowledged by virologist Joseph L. Melnick in 1951.
“There is as yet no clear evidence that the [polio] virus has been obtained in pure form”
Ender’s later admitted that these lab-created effects could not be “considered as necessarily the result of viral activity.”
12 July, 2022 – Toxicology vs Virology: Rockefeller Institute and the Criminal Polio Fraud
10 August, 2021 – How Flawed WHO Vaccination Policies Led To Polio Paralysis In India In 1970s
Vaccine (and antibiotic injections) associated paralytic Poliomyelitis (VAPP)
The Economist explains – What is vaccine-derived polio?
The Economist explains – What is vaccine-derived polio?.pdf
Routine vaccinations and child survival_ follow up study in Guinea-Bissau, West Africa..
The Introduction of Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis and Oral Polio Vaccine Among Young Infants.
The Introduction of Diphtheria-Tetanus-Pertussis and Oral Polio Vaccine Among Young Infants in an Urban African Community.pdf
The relation of prophylactic inoculations to the onset of poliomyelitis: a study of 620 cases in the victorian epidemic of poliomyelitis in 1949.
The relation of prophylactic inoculations to the onset of poliomyelitis_ a study of 620 cases in the victorian epidemic of poliomyelitis in 1949 – PubMed.pdf
Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis: a retrospective cohort study of acute flaccid paralyses in Brazil
Vaccine-associated paralytic poliomyelitis_ a retrospective cohort study of acute flaccid paralyses in Brazil _ International Journal of Epidemiology _ Oxford Academic.pdf
What Polio Vaccine Injury Looks Like, Decades Later.
What Polio Vaccine Injury Looks Like, Decades Later • Children’s Health Defense.pdf
Correlation between Non-Polio Acute Flaccid Paralysis Rates with Pulse Polio Frequency in India.
The Polio & “Non-Polio” Shell Game in Africa & U.S. – 2020 Update
How the CDC Made 30,000 Polio Diagnoses Disappear
Getting Polio from the Polio Vaccine
Paralytic Poliomyelitis Associated With Sabin Monovalent and Bivalent Oral Polio Vaccines in Hungary
Paralytic Poliomyelitis Associated With Sabin Monovalent and Bivalent Oral Polio Vaccines in Hungary _ American Journal of Epidemiology _ Oxford Academic.pdf
Polio programme: let us declare victory and move on
Polio programme_ let us declare victory and move on _ Indian Journal of Medical Ethics
Support for children identified with acute flaccid paralysis under the global polio eradication programme in Uttar Pradesh, India a qualitative study
Support for children identified with acute flaccid paralysis under the global polio eradication programme in Uttar Pradesh, India_ a qualitative study _ BMC Public Health _ Full Text.pdf
WHO: Polio Outbreak in Sudan Caused by Oral Polio Vaccine
Hundreds of Pakistani children hospitalized with nausea and vomiting, following polio vaccines
Hundreds of Pakistani children hospitalized with nausea and vomiting, following polio vaccines – New York Daily News.pdf
Polio Eradication Stalls with More Wild-Type and Vaccine Strain Polio Outbreaks
“Vaccine-Derived” Polio on the Rise
Britain, 1912 to 1963 Pesticides and Polio.
Polio & The Poisoning of America
Polio & The Poisoning of America – The Other Side of Vaccines.pdf
13 March, 2021 – Dismantling the matrix of “everybody knows” – Here’s a mindblower for you
Feb 19, 2025 – Polio’s Vanishing Act
Before the vaccine, temporary muscle weakness sufficed for a polio diagnosis. Afterward, only cases with paralysis lasting 60+ days counted.
Those cases were relabeled as viral/aseptic meningitis, transverse myelitis, Guillain-Barré, and more.